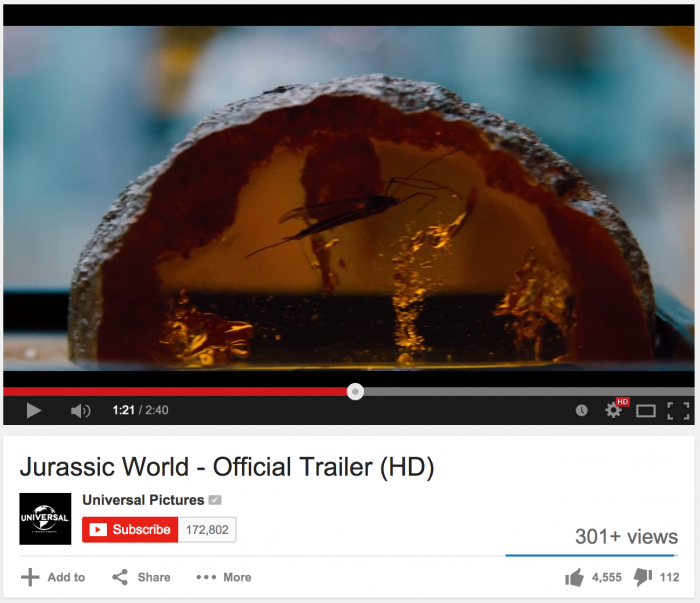The trailer for Jurassic World, the latest instalment in the Jurassic Park franchise, was released today, and well… see for yourself.
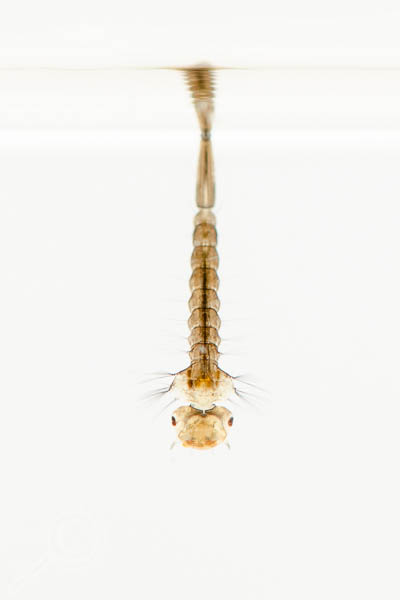
While scientists have apparently figured out how to genetically modify dinosaurs (which I thought was the entire premise of the original when they spliced frog DNA into ancient Dino DNA, but whatever, GM-OH NOES!), they still haven’t hired an entomologist to tell them which amber inclusions are mosquitoes (family Culicidae), and which are crane flies (family Tipulidae).
No big deal though, crane flies and mosquitoes are close enough, right? Well, actually they’re about as closely related to one another as velociraptors are to sea turtles (and only a little more closely related than humans are to Tyrannosaurus rex).
I think we can all agree that Jurassic World would have a much different mood if it climaxed with this
than it does with this

So for all you Hollywood producers out there looking for an entomology consultant to save you from embarrassing oversights, have your people call my people; we can fix this. But in the meantime, save me a seat when Jurassic World hits theatres.
—-
P.S. About that Mosasaur. While we know marine mammals like killer whales can be bitten by mosquitoes (a captive killer whale in San Antonio contracted and later died of West Nile Virus back in 2007), the odds of a mosquito biting a wild mosasaur in the ocean, and then flying, fully leaden with blood, back to shore, only to be immediately entombed in sap running down a tree trunk and preserved for a few million years as an amber inclusion, are a bit of a stretch.
There’s a chance I may be overthinking this.